What is Interstitial electrostimulation (IES)?
Interstitial electrostimulation (IES) is a highly effective way of treating many spine and joints diseases manifestation. The method was developed in Ural state medical Academy by head of traumatology and orthopedics department , academician of RAMS, Professor A. A. Gerasimov. The method have successfully been applied in various medical institutions for more than 20 years.
According to recent scientific researches the cause of pain in the spine and joints is inadequate nutrition of bone and cartilage. Interstitial electrostimulation allows to bring a healing factor - low frequency and high amplitude electrical current directly to the lesion – sore area of the bone. The conductor of this «useful» current is a disposable needle, which pierces the skin, eliminating the electrical resistance of the soft tissues in the path of the current. Due to this fact, the current arrives to bone almost unchanged, increasing the blood supply and nervous provision in the pathological foci. As a result of exposure to nerve receptors the conductivity of nerve impulses restores, improves microcirculation in the vertebrae and joints, prevents the disintegration of cartilage of the intervertebral discs and articular surfaces. Pathological muscle tension and inflammatory soft tissue swelling disappears and, consequently, pain syndrome eliminates.
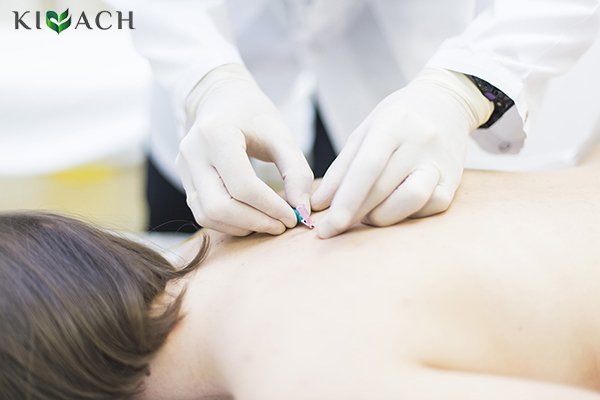
Lesions of the spine indirectly leads to diseases of internal organs. Since all of the organs are innervated by certain sections of the spinal cord, in case of osteochondrosis, due to an impairment of blood supply, development of local edema, constant muscle tension the compression of the nerves of the corresponding segment occurs, which leads to violation of the sympathetic innervation of a certain organ. The imbalance between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system leads to the development of various diseases such as gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, bronchial asthma, neurocirculatory dystonia, depression, asthenia, and some other. IES activates the sympathetic nervous system, which eliminates the Central mechanism of development of these diseases.
During the procedure the patient feels a comfortable sensation of vibration, tingling or pressure.
Interstitial electrostimulation can be applied in combination with other treatment methods (hirudotherapy, massage, hydrotherapy, chiropractic treatment, reflexology, homeopathy
Indications for procedure
- osteochondrosis of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar);
- deforming osteochondrosis;
- arthrosis (joint disease);
- heel spurs;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine, hypotension;
- nerves’ damage;
- asthma and broncho obstructive syndrome
- gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, gastritis;
- prostatitis, erectile dysfunction.
Contraindications
- cancer, blood diseases;
- pregnancy;
- infectious diseases in the acute stage;
- cardiac or pulmonary failure higher than 2nd degree;
- hypertension (systolic a/p above 180 mm of mercury. article);
- individual intolerance of current;
- diffuse-nodular goiter II-III;
- prostate adenoma;
- endoprostheses of large joints of the limbs;
- uterine fibroids in the stage of progression.
Possible reactions
IES procedure is well tolerated by patients, but in some cases, there is a possibility of reactions associated with the individual characteristics of each person.
- local reaction in the form of pain and/or swelling on the place of needle puncture that is connected with the effect on nerve receptors of the skin;
- hematoma in the region of needle puncture;
- increase or decrease of blood pressure;
- short-term weakness, dizziness;
- short-term blood oozing from the place of needle puncture;
- trace reactions such as keloid hem; and others;

